Rendering - Part 2
Following on from creating our 2d pixel buffer in Part 1, we start by splitting the drawing functions into a separate seperate source code file called render.rs - main.rs will now contain our test and exploration code to illustrate the wrok we are doing.
In part 01 we added functions for handling the new pixel buffer and drawing a rudimentory square. In this part we add
draw_pixel to draw a singel pixel at an x,y location for a given RGBA colour.
draw_line uses draw_pixel to draw a line between two x,y points.
draw_triangel and draw_rect use draw_line to draw a triangle or rectangle from provided points.
The draw_square function will probably get depricated because it does not follow the principles of the other draw functions.
The Rust code render.rs
// Adding render functions to minifb
// by Rich of maths.earth 202500308
/// A struct to represent an RGBA pixel.
#[derive(Clone, Copy)]
pub struct Pixel {
pub r: u8,
pub g: u8,
pub b: u8,
pub a: u8,
}
impl Pixel {
/// Create a new Pixel with the given RGBA values.
pub fn new(r: u8, g: u8, b: u8, a: u8) -> Self {
Self { r, g, b, a }
}
/// Convert this pixel into a 32-bit colour in 0xAARRGGBB format.
pub fn to_u32(self) -> u32 {
((self.a as u32) << 24) | ((self.r as u32) << 16) | ((self.g as u32) << 8) | (self.b as u32)
}
}
/// Clears the given 2D pixel buffer by filling every pixel with black.
pub fn clear_buffer(buffer: &mut Vec>) {
for row in buffer.iter_mut() {
for pixel in row.iter_mut() {
*pixel = Pixel::new(0, 0, 0, 255);
}
}
}
/// Draw a square into the provided 2D pixel buffer.
///
/// * `x` and `y` are the top-left coordinates of the square.
/// * `square_width` and `square_height` specify its dimensions.
/// * `color` is the colour to draw.
pub fn draw_square(
buffer: &mut Vec>,
x: usize,
y: usize,
square_width: usize,
square_height: usize,
color: Pixel,
) {
for j in y..(y + square_height) {
for i in x..(x + square_width) {
// Ensure we remain within bounds.
if j < buffer.len() && i < buffer[j].len() {
buffer[j][i] = color;
}
}
}
}
/// Draw a single pixel into the provided 2D pixel buffer.
pub fn draw_pixel(
buffer: &mut Vec>,
x: usize,
y: usize,
color:
Pixel
) {
if y < buffer.len() && x < buffer[y].len() {
buffer[y][x] = color;
}
}
/// Draw a line in to the provided 2D pixel buffer.
pub fn draw_line(
buffer: &mut Vec>,
x0: i32,
y0: i32,
x1: i32,
y1: i32,
color: Pixel,
) {
// Calculate the differences.
let delta_x = x1 - x0;
let delta_y = y1 - y0;
// Determine the number of steps needed based on the longest side.
let longest_side_length = if delta_x.abs() >= delta_y.abs() {
delta_x.abs()
} else {
delta_y.abs()
};
// If the line is just a point, draw that pixel.
if longest_side_length == 0 {
draw_pixel(buffer, x0 as usize, y0 as usize, color);
return;
}
// Calculate the increments for each step.
let x_inc = delta_x as f32 / longest_side_length as f32;
let y_inc = delta_y as f32 / longest_side_length as f32;
// Initialise the current position.
let mut current_x = x0 as f32;
let mut current_y = y0 as f32;
// Draw pixels along the line.
for _ in 0..=longest_side_length {
let ix = current_x.round() as usize;
let iy = current_y.round() as usize;
draw_pixel(buffer, ix, iy, color);
current_x += x_inc;
current_y += y_inc;
}
}
/// Draw a triangle in to the provided 2D pixel buffer.
pub fn draw_triangle(
buffer: &mut Vec>,
x0: i32,
y0: i32,
x1: i32,
y1: i32,
x2: i32,
y2: i32,
color: Pixel,
) {
draw_line(buffer, x0, y0, x1, y1, color);
draw_line(buffer, x1, y1, x2, y2, color);
draw_line(buffer, x2, y2, x0, y0, color);
}
/// Draw a rectangle in to the provided 2D pixel buffer.
pub fn draw_rect(
buffer: &mut Vec>,
x: i32,
y: i32,
width: i32,
height: i32,
color: Pixel
) {
draw_line(buffer, x, y, x + width, y, color);
draw_line(buffer, x + width, y, x + width, y + height, color);
draw_line(buffer, x + width, y + height, x, y + height, color);
draw_line(buffer, x, y + height, x, y, color);
}
/// Converts a 2D pixel buffer into a 1D vector of u32 values (0xAARRGGBB).
pub fn buffer_to_u32(buffer: &Vec>) -> Vec {
let mut flat: Vec = Vec::with_capacity(buffer.len() * buffer[0].len());
for row in buffer {
for &pixel in row {
flat.push(pixel.to_u32());
}
}
flat
}
The Rust code main.rs
// testing our render functions with minifb
// by Rich of maths.earth 202500308
extern crate minifb;
use minifb::{Key, Window, WindowOptions};
// Import our rendering module.
mod render;
use render::{buffer_to_u32, clear_buffer, draw_square, draw_pixel, draw_line, draw_triangle, draw_rect, Pixel};
// Public constants for the window dimensions.
pub const WIDTH: usize = 800;
pub const HEIGHT: usize = 600;
fn main() {
// Create a new window.
let mut window = Window::new(
"Lesson One: 2D Pixel Buffer Rendering with minifb (Library Example)",
WIDTH,
HEIGHT,
WindowOptions::default(),
)
.expect("Unable to create window");
// Create a 2D pixel buffer initialised to black.
// Each pixel is stored as a Pixel struct.
let mut pixel_buffer: Vec> = vec![vec![Pixel::new(0, 0, 0, 255); WIDTH]; HEIGHT];
// Define the dimensions of the square.
let square_width = 100;
let square_height = 100;
// Calculate the top-left corner so that the square is centred.
let square_x = (WIDTH - square_width) / 2;
let square_y = (HEIGHT - square_height) / 2;
// Set the initial square colour to red.
let mut square_color = Pixel::new(255, 0, 0, 255);
// Colour state: 0 = red, 1 = green, 2 = blue.
let mut color_state: u32 = 0;
// Variable to detect key transitions for the space bar.
let mut prev_space_down = false;
// Main loop.
while window.is_open() && !window.is_key_down(Key::Escape) {
// Check the current state of the space bar.
let current_space = window.is_key_down(Key::Space);
// If space has just been pressed (transition from not pressed to pressed)...
if current_space && !prev_space_down {
// Cycle the square colour.
color_state = (color_state + 1) % 3;
square_color = match color_state {
0 => Pixel::new(255, 0, 0, 255), // Red
1 => Pixel::new(0, 255, 0, 255), // Green
2 => Pixel::new(0, 0, 255, 255), // Blue
_ => Pixel::new(255, 0, 0, 255), // Fallback to red (should not occur)
};
}
// Save the current space state for the next iteration.
prev_space_down = current_space;
// Clear the pixel buffer (fill with black).
clear_buffer(&mut pixel_buffer);
// Draw the square into the pixel buffer using the current square colour.
draw_square(&mut pixel_buffer, square_x, square_y, square_width, square_height, square_color);
// Draw a single pixel into the pixel buffer.
draw_pixel(&mut pixel_buffer, 10, 10, Pixel::new(255, 255, 255, 255));
// Draw a line into the pixel buffer.
draw_line(&mut pixel_buffer, 100, 100, 200, 200, Pixel::new(255, 255, 255, 255));
draw_line(&mut pixel_buffer, 180, 100, 280, 280, Pixel::new(255, 0, 0, 255));
// Draw a triangle into the pixel buffer.
draw_triangle(&mut pixel_buffer, 400, 400, 500, 400, 450, 500, Pixel::new(0, 255, 0, 255));
// Draw a rectangle into the pixel buffer.
draw_rect(&mut pixel_buffer, 600, 400, 100, 100, Pixel::new(0, 0, 255, 255));
// Convert the 2D pixel buffer to a 1D u32 buffer.
let buffer = buffer_to_u32(&pixel_buffer);
// Update the window with the new 1D pixel buffer.
// minifb handles double buffering internally.
window
.update_with_buffer(&buffer, WIDTH, HEIGHT)
.expect("Failed to update window");
}
}
Cargo.toml
[package] name = "minifb-rgb" version = "0.1.0" edition = "2024" [dependencies] minifb = "0.28.0"
The image produced:
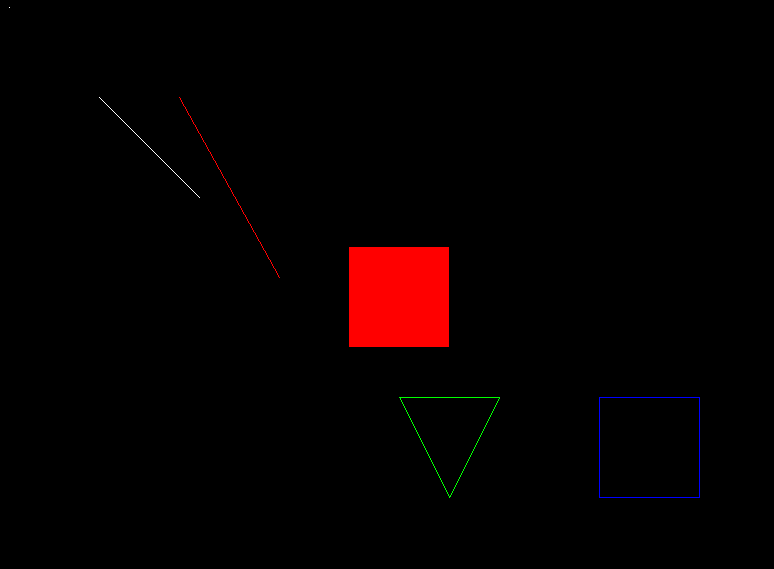
Mission Accomplished
And there we have it, we can draw pixels, lines, triangles and rectangles.